- Call for Service! +91 (0)11 43565446
- Email : safety-india@sigma-hse.com
Standards
VDI 2263 and BS EN 17077
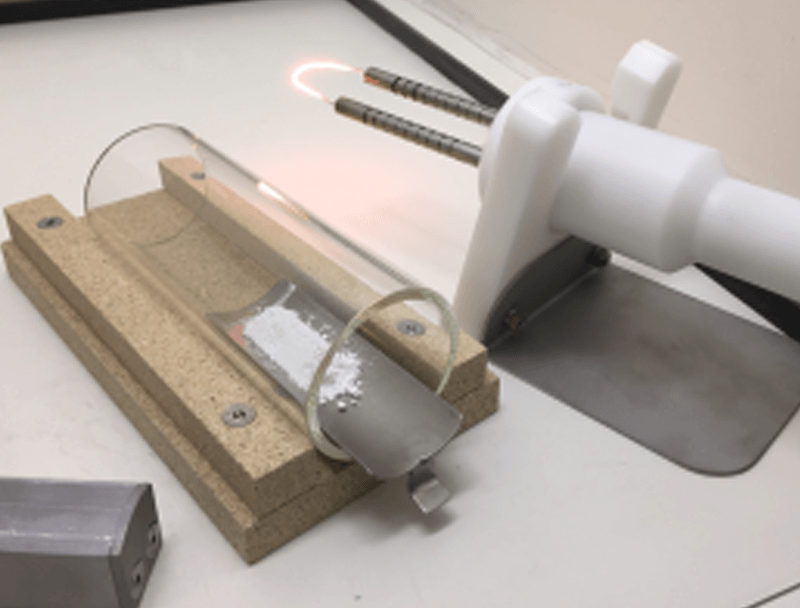
BURNING BEHAVIOUR TESTING PROCESS
The test is conducted to assess the behaviour (severity) of combustion propagation through a material deposit on being ignited by an external ignition source. A small powder strip is formed onto a heat resistant, non-porous plate and ignition trials are performed using a hot (1000°C) platinum wire. Its burning behaviour is numerically rated from 1 (material does not ignite) to 6 (supports rapid combustion) in accordance with the test standards characterisation table. The rating is known as “CC” or Combustibility Class and testing is performed at ambient and elevated environmental temperature conditions.
| Type of Reaction | CC | Reference Product | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No spreading of fire | No Ignition | 1 | Table Salt |
| Brief ignition and rapid extinction | 2 | Tartaric Acid | |
| Localised combustion or glowing with practically no spreading | 3 | Lactose | |
| Fire spreads | Glowing without sparks, (smoldering) or slow decomposition without flame | 4 | Tobacco |
| Burning with flame or spark generation | 5 | Sulphur | |
| Very rapid combustion with flame propagation or rapid decomposition without flame | 6 | Black Powder | |
Benefits
When the burning behaviour of a solid material is known, fires and explosions caused as a result of the introduction of hot embers or friction heat (on bearing failure) can be predicted and therefore either avoided or mitigated. It also can be used as a screening tool to highlight materials that should be classified as a ‘flammable solid’ for transportation